
Julia just finished conducting a coding contest, and she needs your help assembling the leaderboard! Write a query to print the respective hacker_id and name of hackers who achieved full scores for more than one challenge. Order your output in descending order by the total number of challenges in which the hacker earned a full score. If more than one hacker received full scores in same number of challenges, then sort them by ascending hacker_id.
Input Format
The following tables contain contest data:
- Hackers: The hacker_id is the id of the hacker, and name is the name of the hacker.

- Difficulty: The difficult_level is the level of difficulty of the challenge, and score is the maximum score that can be achieved for a challenge at that difficulty level.

- Challenges: The challenge_id is the id of the challenge, the hacker_id is the id of the hacker who created the challenge, and difficulty_level is the level of difficulty of the challenge.

- Submissions: The submission_id is the id of the submission, hacker_id is the id of the hacker who made the submission, challenge_id is the id of the challenge that the submission belongs to, and score is the score of the submission.

Sample Input
Hackers Table:
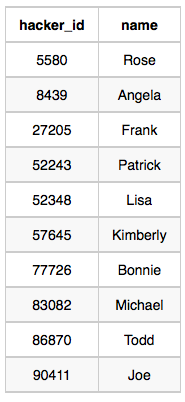
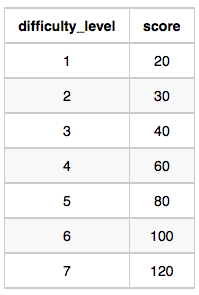
Difficulty Table:
Challenges Table:

Submissions Table:

Explanation
Hacker 86870 got a score of 30 for challenge 71055 with a difficulty level of 2, so 86870 earned a full score for this challenge.
Hacker 90411 got a score of 30 for challenge 71055 with a difficulty level of 2, so 90411 earned a full score for this challenge.
Hacker 90411 got a score of 100 for challenge 66730 with a difficulty level of 6, so 90411 earned a full score for this challenge.
Only hacker 90411 managed to earn a full score for more than one challenge, so we print the their hacker_id and name as space-separated values.
Julia는 자신이 주최한 코딩 대회의 리더보드를 만들고자 합니다. 조건은 다음과 같습니다:
- 한 명의 해커가 2개 이상의 문제에서 만점을 받은 경우만 리더보드에 포함시킵니다.
- 출력은 다음과 같은 우선순위로 정렬됩니다:
- 만점 받은 문제 수 (내림차순)
- 동일할 경우, hacker_id 오름차순
SELECT s.hacker_id, h.name
FROM Submissions s
JOIN Challenges c ON s.challenge_id = c.challenge_id
JOIN Difficulty d ON c.difficulty_level = d.difficulty_level
JOIN Hackers h ON s.hacker_id = h.hacker_id
WHERE s.score = d.score
GROUP BY s.hacker_id, h.name
HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT s.challenge_id) > 1
ORDER BY COUNT(DISTINCT s.challenge_id) DESC, s.hacker_id;| JOIN | 제출 → 문제 → 난이도 → 해커 이름을 연결하기 위해 여러 테이블을 조인합니다. |
| WHERE s.score = d.score | 해당 제출이 문제의 만점과 일치하는 경우만 필터링합니다. |
| GROUP BY s.hacker_id, h.name | 해커별로 그룹화해서 만점 받은 문제 개수를 세기 위해 사용합니다. |
| HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT s.challenge_id) > 1 | 한 해커가 2개 이상의 문제에서 만점을 받은 경우만 남깁니다. |
| ORDER BY COUNT(...) DESC, s.hacker_id | 먼저 만점 문제 개수 기준 내림차순, 동일 시 hacker_id 오름차순으로 정렬합니다. |
'Computer Science > SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SQL | HackerRank 가장 많이 챌린지를 만든 학생 구하기 (0) | 2025.06.22 |
|---|---|
| SQL | HackerRank Ollivander’s Inventory (0) | 2025.06.21 |
| SQL | HackerRank 성적에 따라 이름을 보여주는 리포트 만들기 CASE WHEN (0) | 2025.06.19 |
| SQL | HackerRank ROW_NUMBER()와 COUNT(*) OVER()를 활용하여 중앙값(Median) 구하기 (0) | 2025.06.18 |
| SQL | HackerRank 평균 오차 구하기 (Replace) (0) | 2025.06.17 |