
Julia asked her students to create some coding challenges. Write a query to print the hacker_id, name, and the total number of challenges created by each student. Sort your results by the total number of challenges in descending order. If more than one student created the same number of challenges, then sort the result by hacker_id. If more than one student created the same number of challenges and the count is less than the maximum number of challenges created, then exclude those students from the result.
Input Format
The following tables contain challenge data:
- Hackers: The hacker_id is the id of the hacker, and name is the name of the hacker.

- Challenges: The challenge_id is the id of the challenge, and hacker_id is the id of the student who created the challenge.

Sample Input 0
Hackers Table:
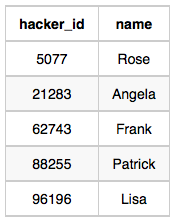
Challenges Table:
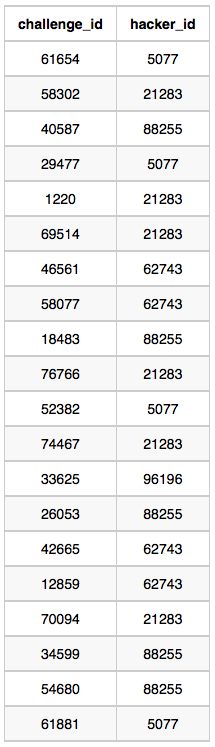
Sample Output 0
21283 Angela 6
88255 Patrick 5
96196 Lisa 1
Sample Input 1
Hackers Table:

Challenges Table:

Sample Output 1
12299 Rose 6
34856 Angela 6
79345 Frank 4
80491 Patrick 3
81041 Lisa 1
Explanation
For Sample Case 0, we can get the following details:
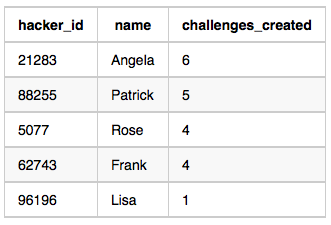
For Sample Case 1, we can get the following details:

Julia는 학생들에게 코딩 챌린지를 만들도록 시켰고, 이제 누가 몇 개의 챌린지를 만들었는지 정리하려고 합니다. 이 글에서는 SQL을 사용하여 학생별 챌린지 개수를 세고, 특정 조건에 맞게 결과를 필터링하는 쿼리를 작성해보겠습니다.
- 각 해커의 hacker_id, name, 총 챌린지 개수를 출력합니다.
- 챌린지 수 기준 내림차순, 동률일 경우 hacker_id 오름차순으로 정렬합니다.
- 단, 최다 챌린지를 만든 학생은 모두 포함하지만, 그보다 적은 수를 만들었더라도 동률이면 결과에서 제외합니다.
SELECT h.hacker_id, h.name, COUNT(c.challenge_id) AS total_challenges
FROM Hackers h
JOIN Challenges c ON h.hacker_id = c.hacker_id
GROUP BY h.hacker_id, h.name
having
count(c.challenge_id) = (
select max(challenge_count)
from (
select count(*) as challenge_count
from Challenges
group by hacker_id
)as sub
)
or count(c.challenge_id) in (
SELECT challenge_count
FROM (
SELECT COUNT(*) AS challenge_count
FROM Challenges
GROUP BY hacker_id
) AS sub
GROUP BY challenge_count
HAVING COUNT(*) = 1
)
ORDER BY total_challenges DESC, h.hacker_id;- Challenges 테이블을 해커별로 GROUP BY하여 챌린지 개수를 구합니다.
- HAVING절로 다음 두 조건 중 하나를 만족하는 해커만 필터링합니다:
- 챌린지 수가 최대값과 같음
- 챌린지 수가 유일함 (즉, 동점자가 아님)
- 정렬 조건을 맞춰 출력합니다.
COUNT(c.challenge_id) = (
SELECT MAX(challenge_count)
FROM (
SELECT COUNT(*) AS challenge_count
FROM Challenges
GROUP BY hacker_id
) AS sub
)- 모든 해커의 챌린지 개수(challenge_count) 중 최댓값을 구합니다.
- 그 최댓값과 같은 수의 챌린지를 만든 해커들은 모두 포함합니다.
- → 즉, 최고 성과자는 전부 보여줘!
| 12299 | 6 ← 포함 |
| 34856 | 6 ← 포함 |
| 79345 | 4 ← 다음 조건으로 판단 |
OR COUNT(c.challenge_id) IN (
SELECT challenge_count
FROM (
SELECT COUNT(*) AS challenge_count
FROM Challenges
GROUP BY hacker_id
) AS sub
GROUP BY challenge_count
HAVING COUNT(*) = 1
)- 이 조건은 최댓값 이외의 값들 중에서, 오직 한 명만 있는 경우만 포함합니다.
- GROUP BY challenge_count → 개수별로 묶고
- HAVING COUNT(*) = 1 → 그 개수를 가진 해커가 1명일 때만 통과
- → 즉, 나 혼자 3개 만들었으면 OK, 둘 이상이면 제외
| 챌린지 개수 | 인원 수 |
| 6 | 2명 ← 최댓값이므로 포함됨 |
| 4 | 1명 ← 포함됨 (유일) |
| 3 | 3명 ← 제외됨 (동점자 있음) |
'Computer Science > SQL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SQL | HackerRank 각 해커의 챌린지별 최고 점수 합계 구하기 (0) | 2025.06.23 |
|---|---|
| SQL | HackerRank Ollivander’s Inventory (0) | 2025.06.21 |
| SQL | HackerRank 코딩 대회에서 여러 문제를 만점 받은 참가자 찾기 (2) | 2025.06.20 |
| SQL | HackerRank 성적에 따라 이름을 보여주는 리포트 만들기 CASE WHEN (0) | 2025.06.19 |
| SQL | HackerRank ROW_NUMBER()와 COUNT(*) OVER()를 활용하여 중앙값(Median) 구하기 (0) | 2025.06.18 |